Effective maintenance, encompassing predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance, is crucial for sustaining the continuous and optimal functionality of an organization’s systems, machinery, equipment, and assets. It’s an integral aspect of asset management. Lack of a maintenance plan may lead facility owners to encounter substantial downtimes and expensive repairs. However, the efficacy of planned maintenance hinges on the specific strategy adopted.
Some plant operators fix equipment failures only after the machinery malfunctions or break down. In contrast, others check the equipment well before it is in disrepair. There are many ways to plan maintenance, so knowing which one is best can be challenging. Most companies choose proactive maintenance strategy approaches. But, between the two most common, predictive and preventive, which one is better?
What Are the 4 Types of Maintenance?
Plant managers and operations professionals follow different plans to keep assets in good working order. Strategies and tools will vary depending on an organization’s assets, budget, and other aspects of its operations. There are four basic types of maintenance strategies for asset management:
- Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
- Corrective Maintenance (CM)
- Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
- Preventive Maintenance (PM)
Some plants take a “reactive” approach (condition-based maintenance or corrective maintenance), only fixing equipment after it malfunctions or breaks down. Other plant operators take a “proactive” approach (predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance) and check equipment well before it is in disrepair. While a reactive strategy has its place in some operations plans — it’s better than a no-maintenance strategy — there’s a clear advantage to being proactive and avoiding issues altogether.
What Is the Difference Between Predictive Maintenance and Preventive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance are both proactive approaches to keeping equipment well-maintained. Maintenance managers can use them with some of the more reactive strategies. However, as factories and plants grow, the technology and equipment become much more complex.
Operations managers often find they need to employ more advanced maintenance strategies. Because of cost and associated risks, one needs to weigh the pros and cons of each method before making a final decision.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is an advanced method of maintenance that uses artificial intelligence (AI) for optimal upkeep. Plant managers can identify issues through the real-time collection and analysis of operational data. Workers conduct predictive maintenance tasks on an as-needed basis. The most tech-savvy teams use predictive maintenance strategies.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance (or preventative maintenance) involves a cycle of tasks performed on a set schedule. Machine operators conduct preventive duties regardless of equipment needs to keep all parts in good condition. Sometimes, a computerized scheduled maintenance management system (CMMS) may help workers complete work orders. Managers typically use a CMMS with equipment involving condition-based sensors and integrated maintenance software. Of the many types of proactive strategies, preventive maintenance is the most popular.
What Are the Advantages of Predictive Maintenance?
There are many advantages to taking a predictive approach to machinery upkeep. The predictive system employs condition-based maintenance powered by technology. Maintenance managers can quickly perform repairs while a machine is still running or shut down. This asset management approach leads to improvements in everything from maintenance cost savings to risk reduction.
A recently published report highlighted many of the advantages of predictive maintenance. Based on results outlined in Digital Industrial Revolution with Predictive Maintenance, plants and factories that use predictive maintenance can expect to achieve the following outcomes:
- 12% cost savings
- 9% uptime improvement
- 14% reduction in risks (safety, health, environment, and quality)
- 20% lifetime extension of aging assets
In contrast, workers perform preventive maintenance tasks that are scheduled based on time rather than conditions, which can lead to unnecessary maintenance. The scheduled maintenance approach also neglects to consider the current state of the equipment or the process.
As opposed to reactive maintenance strategies, preventative measures can decrease maintenance expenses and reduce the risk of equipment failures. However, predictive maintenance can lead to even greater cost savings despite requiring more capital and time to implement.
What Are Examples of Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance has a wide range of use cases spanning many industries. To collect data, maintenance managers may use any of several devices:
- Condition-Monitoring Devices — These devices have sensors to collect information about the equipment’s performance, such as pressure, temperature, vibration, and noise.
- Internet of Things (IoT) — This internet-based system translates sensor data into signals that can help predict when equipment needs fixing.
- Machine Learning — This approach uses sensor data to learn typical equipment performance for identifying anomalies and predicting issues.
- Computerized Maintenance Management System — A CMMS generates maintenance work orders for repairs.
For example, in the food and beverage industry, businesses that deal with food products must ensure consumers’ health and safety and reduce the risk of liability. Predictive maintenance can identify when equipment is not working correctly, such as refrigeration systems designed to keep food at specific temperatures.
In the manufacturing industry, product manufacturers often rely on equipment that is both large and expensive. Even the most minor technical failure can lead to an immense loss when production slows down or comes to a complete halt. For this reason, predictive maintenance software applications are crucial in signaling issues before they become out of control and lead to a high-maintenance cost to fix.
How AI is shaping the future of Predictive maintenance
Challenges with Traditional Predictive Maintenance

Traditional predictive maintenance solutions produce
- Too many alarms
- No diagnosis and requires experts to connect the alarms
- Highly manual and inefficient
- Don’t work after the vendor leaves
UptimeAI enables the following:
- Reduction of alarms by monitoring larger systems
- Built-in 1000+ failure modes/diagnosis
- Auto false alarm correction and high automation
- Easier to maintain and use
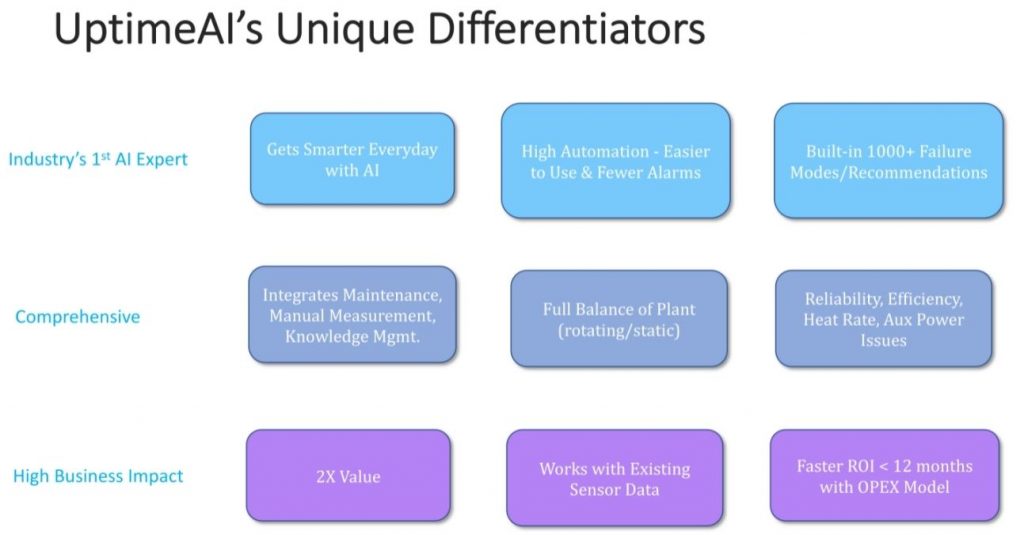
UptimeAI provides trusted solutions for effective plant operations by leveraging technological advances in artificial intelligence. We are the industry’s first AI expert, so you can trust that we’ll implement comprehensive solutions with high business impact. If you’re looking for assistance with taking a predictive approach to your maintenance plan, book a demo today!
